Ontotext GraphDB and the Ontotext Platform
Update solution on January 31, 2024
What is it?
GraphDB is a native RDF graph database with dynamic indexing that integrates with various search technologies (most notably Elastic Search), document stores (MongoDB), and text mining. There is a developer edition (GraphDB Free Edition) that is free but limited by the fact that it is not available on the cloud, and also that it lacks commercial support and high availability features. These deficits are rectified by the commercially-available GraphDB Enterprise Edition (EE). GraphDB EE has recently been released on both the AWS and Azure marketplaces.
GraphDB is part of the Ontotext Platform (see Figure 1), a set of tools that targets general-purpose data management and text analytics based on the use of knowledge graphs. It features various add-ons and tools from Ontotext and its partners that provide a variety of capabilities. These include the Ontotext-developed Metadata Studio, a text analysis environment, and Ontopic, a partner-developed tool for data virtualisation. The latter, along with the platform’s JDBC driver and Kafka connector, offer a framework for upstream and downstream integration with SQL data sources, enterprise message buses and BI tools as part of a broader data ecosystem.
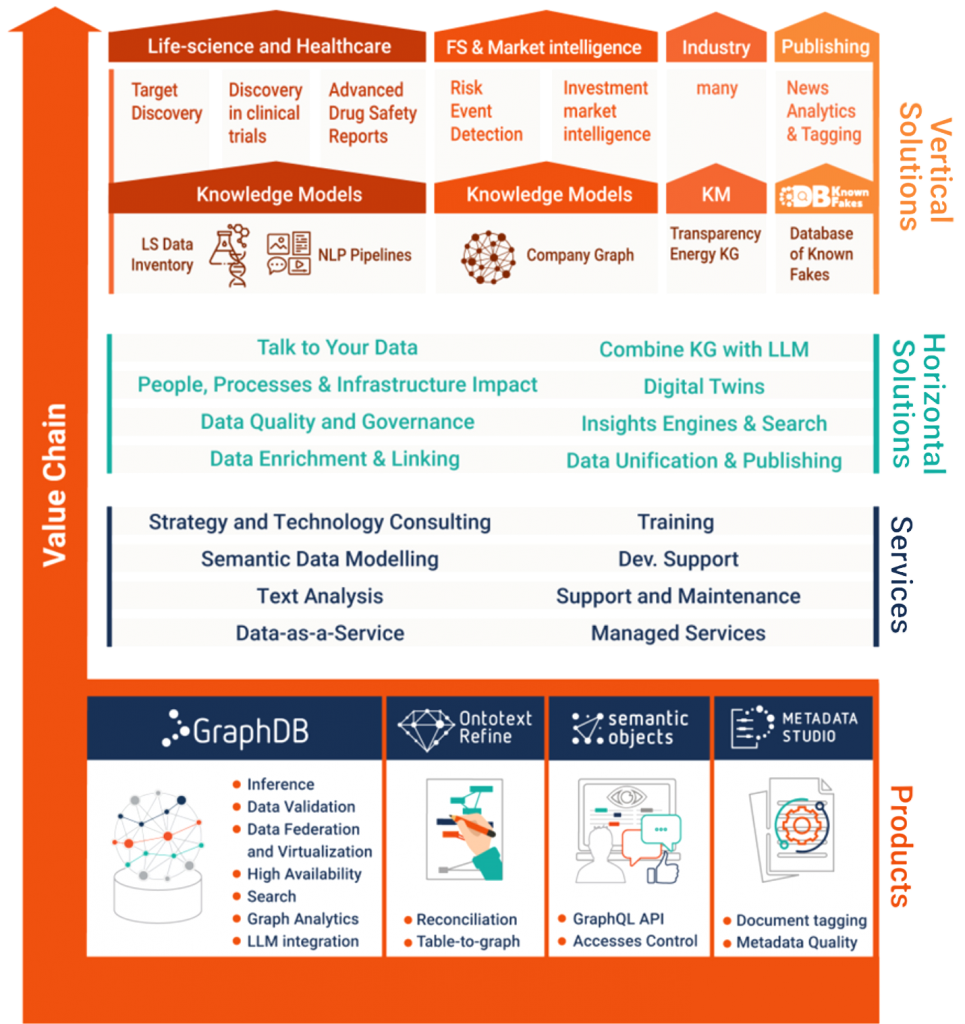
Fig 1 – The Ontotext platform (cutout)
Of particular note is the recent addition of integration with ChatGPT, the now well-known generative AI engine and large language model (LLM), via an OpenAI API. This allows you to interact with your graph via natural language queries and receive a human-readable response generated by ChatGPT in context to it. This can include an explanation of your query results, which may be useful for better understanding your graph. Moreover, Ontotext has recently integrated LLMs into its text analysis stack, GraphDB supports the development of neural networks and LLMs trained on graph data, and vector database integration is available within the platform. In addition, Ontotext has partnered with Novasenta to facilitate predictive analytics in the life sciences domain.
Customer Quotes
“We have used GraphDB with a number of large corporate clients to develop complex Knowledge Graph solutions. GraphDB is a powerful and scalable solution that we are confident to introduce to our most important clients on some of our most important projects.”
Enterprise Knowledge
Mutable Award: Gold 2023
What does it do?
GraphDB includes various capabilities that extend beyond the database, notably ontology visualisation and connectors to a variety of third-party environments (mostly search engines such as Solr, Lucene and ElasticSearch, but also MongoDB). Internally, GraphDB’s inference engine employs forward chaining, and it provides various functions for dealing with materialised inferences which retract inferred statements. Cluster management and performance (including load performance), security (including LDAP and Kerberos support), visualisation capabilities and support for workflow processes to enable the loading of structured data into GraphDB are all major features, as is support for geo-spatial constraints and graph-path search. In addition, GraphDB offers several features for delivering high-availability clusters, including quorum-based replication and node-driven, self-organising leader election.
GraphDB supports RDF* and SPARQL*, which allows you to attach attributes to relationships. This is the equivalent of labels on a property graph, except that RDF* is more expressive. In addition, the company’s implementation of RDF* supports backwards compatibility.
What’s more, Ontotext is intent on making graph applications and analytics really easy to use for developers. For instance, GraphDB supports GraphQL via the Semantic Objects add-on, a framework, that allows the relevant APIs to be automatically created from semantic object descriptions, essentially meaning that developers do not need to know SPARQL. It also provides built-in facilities for data import and reconciliation (now provided as the separate Ontotext Refine tool), querying, search, visualisation, monitoring and cluster management, plus the company focuses on working and integrating with various open-source components. This should all help to provide an easy start for developers.
Why should you care?
Ontotext impresses with its dependable performance and efficient handling of both graph analytics and semantic metadata management. This is borne out through its audited results in both the Semantic Publishing and Social Network LDBC benchmarks.
In addition, Ontotext has the best implementation of RDF* that we have seen, and this combines with the company’s performance on the aforementioned benchmarks (especially the Social Network Benchmark, which is designed to measure graph analytics capability) to give real credence to the idea of using Ontotext for use cases that have traditionally been reserved for property graphs.
The scope of the Ontotext Platform is broader than most anything else in the market (in part thanks to its long list of integrated partners), and we like its support for GraphQL and its integration with open-source technologies of various kinds.
Moreover, GraphDB’s support for generative AI, LLMs and ChatGPT puts it noticeably ahead of the curve when it comes to these areas, which are currently some of the most popular in data.
The Bottom Line
Apart from its domain expertise, Ontotext has historically offered significant capabilities in semantics, search, text mining, and knowledge graphs. Indeed, its continuing emphasis on the latter is both notable and sensible, as it is one of the most sought-after graph use cases. In short, if you have an interest in knowledge graphs, and especially if you have an interest in using them alongside generative AI, you should consider Ontotext.
Related Company
Connect with Us
Ready to Get Started
Learn how Bloor Research can support your organization’s journey toward a smarter, more secure future."
Connect with us Join Our Community
