MongoDB
Update solution on June 27, 2019
MongoDB is an open source, distributed, NoSQL document-oriented database that stores JSON documents. As of version 4.0 (released summer 2018) the product supports multi-document ACID transactions with snapshot isolation. The product is consistent by default but you can choose eventual consistency if you prefer.
Four significant additions to the database are the MongoDB Ops Manager, which does what its name suggests; MongoDB Compass, the graphical user interface, which is used for schema visualisation (you can lock down the schema if you want to) and ad hoc query purposes; the MongoDB Connector for BI, which translates third party (Tableau, Qlik, MicroStrategy and so on) SQL into MongoDB (and MongoDB Atlas) aggregation queries; and MongoDB Charts, which is used to create visualizations of MongoDB data, including complex structures such as arrays and sub-documents. It is currently in beta and available for on premises deployments or fully managed on MongoDB Atlas. It is also worth commenting that while MongoDB Stitch has its own SDK it also supports a MongoDB Wire Protocol.
Customer Quotes
“It’s been fantastic for our developers to build and iterate quickly… MongoDB is also helping us extend that great experience to the scientists and clinicians making it easier and faster for them to find critical insights in the data.”
Genomics England
“The whole emphasis of MongoDB has been, and is, on making life easy for developers. This continues to be the case, regardless of which product you are adopting.”
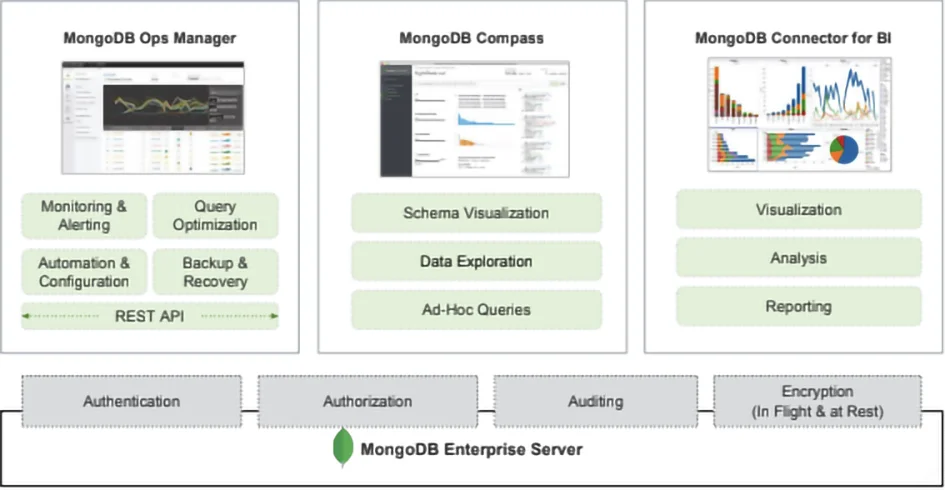
Fig 01 MongoDB editions and additional products available
MongoDB is a scale-out NoSQL database that makes use of in-memory techniques. Nodes in a cluster can be distributed geographically. In a hybrid environment you can choose how many (up to 47) nodes should be dedicated to analytics within a single replica set. Sharding is used when you want to partition the data over multiple replica sets: you can run analytics on the secondaries within each replica set to avoid impacting the production workload that’s running on the primaries.

Fig 02 Spark connector
MongoDB supports a very wide range of languages and these include both R and Python, though there is no support for either TensorFlow or PMML (predictive modelling mark-up language). What the company calls its Aggregation Framework, provides a data processing pipeline for both transformations and analytics, which are modular and easy to write and debug. There is also an Aggregation Pipeline Builder available in MongoDB Compass for those who want to explore their data using a tool or who are new to aggregation syntax. More generally, these capabilities are significant because they are part of what makes MongoDB a multi-model database, because it allows you to perform functions such as joins and recursive graph traversals. Thus, MongoDB can also be used to support tabular, key-value, text, geo-spatial and graph models along with relevant analytic capabilities such as faceted search and graph traversals. There is also a shard-aware Spark connector: see Figure 2.
This allows data to be processed in place, in a massively parallel manner, without any need for ETL processes. Aggregation pre-filtering, together with the use of secondary indexes, improves performance. The query optimiser is also shard-aware.
The whole emphasis of MongoDB has been, and is, on making life easy for developers. This continues to be the case, regardless of which product you are adopting. It is particularly evident in MongoDB Stitch because this removes the need to know about application server functions, which are handled automatically.
Historically, MongoDB was best described as an “operational” database if we assume that the distinction between “transactional” and operational systems is that transactions require ACID guarantees. However, that changed with the introduction of MongoDB 4.0 and the incorporation of multi-document ACID transactions, as opposed to these guarantees being limited to within a single document as they were previously. That said, we have the impression that the company is more focused on operational rather than transactional use cases; it frequently states that “most applications won’t require transactions”. Beyond this, the company has introduced extensive analytic support to enable analytic capabilities with the same low latency requirements as its operational/transactional support.
The Bottom Line
MongoDB is the leading document database. If that is your preferred approach to developing applications then you should always be considering MongoDB as a potential provider, regardless of whether you have a hybrid requirement or not. However, there are also strong arguments in favour of considering MongoDB for hybrid transactional and analytic environments even if you have not previously considered the merits of using a document-oriented approach.
Related Company
Connect with Us
Ready to Get Started
Learn how Bloor Research can support your organization’s journey toward a smarter, more secure future."
Connect with us Join Our Community
