Broadcom Test Data Manager
Update solution on February 1, 2024
What is it?
Test Data Manager (TDM) is a test data management solution that uses data subsetting, data masking and synthetic data generation to produce secure, standardised, optimally covering, and up-to-date test data at scale, delivered on-demand via self-service. In the process, it profiles your production data, creating an easily understood view of your data relationships and what data exists where. All of its functionality is delivered through a single, unified web portal, with rich API support, guided workflows, and instructional videos built-in to assist with its operation. Although its most obvious use is to support enterprise-level testing, it has also been deployed to help with data security, regulatory compliance, cloud migration, and machine learning use cases.
It is compatible with a variety of data sources, including DB2, Oracle, SQL Server, and PostgreSQL, and it supports mainframe, cloud, and distributed environments. This selection has recently expanded to cover NoSQL databases, with a comparable level of scalability. Accordingly, the product offers native support for various data types specific to individual NoSQL databases; custom wrappers that are used instead of generic JDBC and ODBC connectors; and an improved engine for synthetic data generation that is optimised for the especially large volumes of data that are often found in NoSQL databases. The product can also operate alongside several third-party applications, and includes accelerator content for applications like SAP.
TDM readily integrates and synergises with other Broadcom testing products, including Agile Requirements Designer and Service Virtualization, by supplying them with reusable, realistic test data. The result is that TDM can be deployed alongside these products to create a broad platform for test automation driven primarily by Broadcom solutions. Integration into a wider testing environment is further supported by built-in data orchestration features that can, for example, be used to perform setup and teardown actions respectively before and after producing your test data. This can be very useful for smoothly incorporating your test data into complex and highly automated continuous testing pipelines.
Customer Quotes
“Test Data Manager has ensured compliance by masking millions of rows of complex sensitive information in minutes. Personal data is replaced with realistic but fictitious values, while maintaining the referential integrity needed for testing across each system.”
Leading Canada Financial Institution
“Test Data Manager has enabled the highest possible performance when extracting small, more intelligent subsets from production.”
Large financial group
“Test Data Manager has helped us speed up testing and fill in missing test scenarios by using synthetic data generation and the masking functionally gives us confidence that our client’s personal information is secure.”
Top 3 US Insurance Company
Mutable Award: Gold 2021
What does it do?
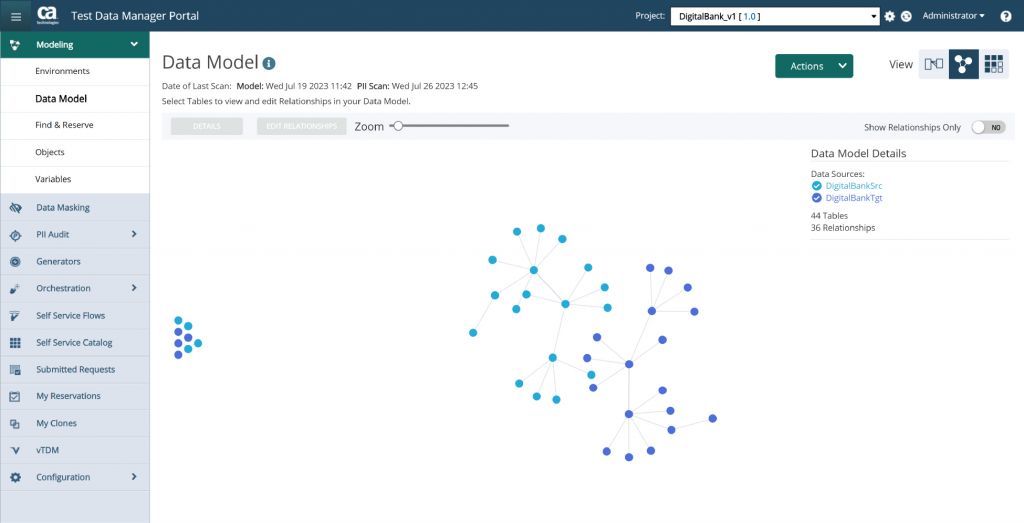
TDM works by automatically building a model of your data and its environment (see Figure 1) then leveraging that model to create test data. It will profile your data and discover the relationships and sensitive data contained therein. It will also produce a variety of visualisations based on your model, such as a heat map that visualises PII hotspots (see Figure 2). There is functionality for creating audit reports for your PII data, which may be helpful for demonstrating regulatory compliance, and there is a unified workflow for profiling, masking, and auditing your data. This workflow ensures that there is a common linkage between the detection of PII data, the remediation of said data, and your continuous compliance processes. Delta-based discovery scans (meaning they only consider data that was added or changed since the last scan took place) are also available, and may be especially useful for supporting agile development.
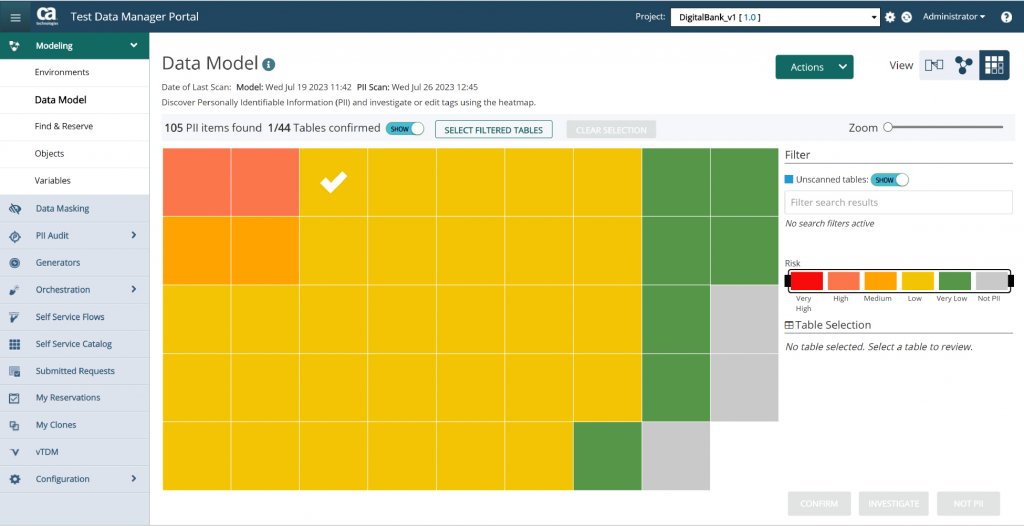
Fig 02 – PII heat map in Broadcom Test Data Manager
Data subsetting is provided, and is supported by rules-driven data masking. Rules can be applied to either columns or tags, with over eighty masking rules provided out of the box (more can be added manually). Masking always maintains referential integrity, preserves the data’s original format, is fully auditable, can be applied to millions of rows in a matter of minutes either in-place or in-flight, and is demonstrably compliant with various mandates (including GDPR) as well as the NIST cybersecurity framework. It can be applied to any number of environments at once, can be scheduled to run automatically, and displays a preview of the end results before committing them. You can also choose to retain your pre-masked data after the process has finished, allowing you to revert the process if necessary. If you change your mind, said data can be deleted easily.
Synthetic data generation is available. It relies on a user-created model of valid test data attributes that, once built, can be used to automatically generate synthetic data sets using either built-in or custom functions. These data sets can achieve up to one hundred percent coverage while still being representative of your production data. This includes generating outliers, edge cases, unexpected results, boundary conditions and negative paths. This process is also resilient in the face of schema changes and the like.
In addition, the product is designed to make test data easily accessible. For example, you can set up self-service and automated delivery of test data to testing teams; the product will dynamically build a test data warehouse (or mart) that functions as a central library of test data that can be reused on demand; and there is a ‘find and reserve’ feature that allows you to prevent data from being modified while you are preparing it for use as test data. Agile development in particular is supported via in-sprint provisioning of test data. Test data can also be delivered using a data cloning process that combines subsetting and synthetic data. This is designed to help data science teams create training data, with one or more subsets forming the bulk of the data set while synthetic data is leveraged to generate “what if?” scenarios and other cases of interest. Broadcom also has plans to exploit generative AI further down the road.
Moreover, instances of TDM can be easily and quickly deployed to multiple testing teams and/or business units with a consistent, templatised configuration via its enterprise configuration deployment functionality. This will be useful if you are moving away from the highly centralised “centre of excellence” model for enterprise test data and are instead looking at something more distributed, wherein test data responsibilities are more likely to be devolved to individual business units.
TDM can (optionally) be deployed via Docker or Kubernetes containers while retaining the bulk of its data masking, data discovery, and synthetic data functionality. Deployment of this kind is highly scalable, capable of parallelising jobs across many separate instances of TDM. Even greater scale is available for data masking in particular, wherein Kubernetes containers equipped with masking functionality are paired with the KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaling) framework to automatically and dynamically provision and/or scale up containers as needed to mask across your enterprise, with minimal manual configuration needed.
Why should you care?
TDM offers particularly mature synthetic data capabilities, including the ability to generate representative synthetic data sets via analysis of your production data. Moreover, this capability is positioned (and delivered) as a viable alternative to subsetting, rather than as merely an addendum to it. Using the two approaches together is also well-supported. In fact, its competitive data subsetting, masking and profiling capabilities in addition to its robust synthetic data generation make it an ideal solution if you want to combine synthetic data and data subsetting within a single platform.
What is more, Broadcom has a pronounced focus on serving large-scale, enterprise clients. TDM’s capabilities have developed accordingly, with this focus coming out in its emphasis on performance at scale and templatised deployment as well as its explicit scalability features, such as its use of KEDA alongside data masking containers. The company has noted that it believes data masking could become a core part of enterprise data security, but that this will only happen if masking at massive scale is a real possibility. Broadcom seems to be well on its way to making that the case.
In fact, this focus is apparent even in the capabilities Broadcom does not meaningfully offer. Database virtualisation, for example: Broadcom does offer a solution, in the form of Virtual Test Data Manager, but it is clear the product has been heavily deemphasised, and is not a priority for the company (and it only supports Oracle and SQL Server, to boot). This seems to be the case in large part because Broadcom does not believe that database virtualisation as a technology can scale up to serving enterprise customers without incurring prohibitive infrastructure costs.
Finally, TDM’s web portal provides a one-stop-shop for test data provisioning, while the test data warehouse, self-service, automated delivery, and find and reserve features facilitate reuse, collaboration, and expedient test creation. These qualities are further enhanced by its integration with Agile Requirements Designer and Service Virtualization, as well as its general capacity for integration and wide range of support for data sources. Its compatibility with NoSQL is especially notable.
The Bottom Line
Test Data Manager is a formidable, highly automated test data management solution that is especially well-equipped to serve clients that operate at enterprise scale.
Related Company
Connect with Us
Ready to Get Started
Learn how Bloor Research can support your organization’s journey toward a smarter, more secure future."
Connect with us Join Our Community
