Blockchain
Last Updated:
Analyst Coverage: David Terrar

Figure 1 – Global Blockchain Technology Market worth $12.48 Billion by 2025 | CAGR: 53.2% (Source: GME)
A blockchain is a distributed ledger, implemented across many networked servers, consisting of a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked across the whole network and secured using cryptography. Control is decentralised so that all of the nodes in the network are capable of adding new blocks. All of the nodes of the network verify every existing and new block. In practice it would be impossible to beat the encryption simultaneously on all nodes, making the ledger tamper proof and therefore immutable.
Why is it important (hot)?
The problem we are solving with blockchain technology is at the heart of all commerce and trade. Trust. The key advantage of using this approach is that the all parties, competitors or even adversaries involved in an exchange of assets, data, goods or services can trust a common digital ledger without the traditional need for any intermediary like a bank or broker or lawyer or government agency needing to be involved to provide oversight. It presents a new paradigm of a trusted peer to peer transaction or asset exchange which is enormously disruptive. It is being deployed to track title-deeds, provenance of diamonds, food traceability, and industry wide regulation. It has the potential to change our personal and business lives over the next 20 years just as much as the Internet has changed business and society over the last 20 years.
Blockchain is often associated with the first cryptocurrency Bitcoin, which was the earliest implementation using this technology, but that is only one of potentially thousands of use cases and solutions that can be built on one of the many different implementations of the blockchain concept. An immutable ledger could be created for property ownership, births, marriages, passports, drivers’ licenses, car registration or voter identification. It will disrupt the banking industry, giving people the ability to sidestep financial institutions to send money cheaply, securely and directly to another person anywhere in the world. It will simplify the world’s supply chain with a level of trust, traceability and transparency that will optimise business transactions and change trading relationships. It will affect every walk of life.
How does it work?
Blockchain databases consist of several, distributed server and storage nodes, all of which participate in the administration and verification of the data all of the time. A traditional database is administered by a central authority giving permission for records to be created, read, updated or deleted, whereas blockchain technology can only create and read. This form of database only allows reading existing blocks and adding or appending additional blocks, as well as cryptographically validating those changes. All of the nodes in the network are capable of adding new blocks. All of the nodes of the network verify every existing and new block. That means that a malicious agent who wants to beat the cryptographic encryption needs to do that on all the nodes of the network simultaneously, making it so difficult and expensive in compute power (with current technology) as to be impossible in practice. That’s why this form of distributed ledger technology can be considered immutable.
It is important to note that while blockchains contain transaction data, they are not a complete replacement for the existing database technology, transaction processing or messaging systems, but they will always sit alongside, connect to and work with those technologies.
We are at the early stages of enterprise use of blockchain. There are already different frameworks with different purposes and potential applications. Examples include Etherium which is usually public (but can be private) and is permissionless so anyone can participate in the network. Hyperledger Fabric and Corda are for private, permissioned networks where participants are selected in advance and access is restricted to these parties only, and there are other examples too. These differences become important as the number of nodes validating blocks on the network has an effect on transaction rate, and scalability is a key issue to be addressed in blockchain’s evolution
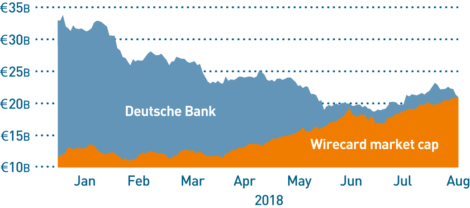
Figure 2 – Wirecard AG valuation vs Deutsche Bank AG valuation – the German fintech card payments company that is deploying blockchain technology now has a higher market value than one of the major world banks. (Source: Bloomberg)
Around 90% of world trade is carried by the international shipping industry. Maersk the world’s largest container shipping firm, in partnership with IBM, have developed and spun off a joint venture called TradeLens which is an open and neutral industry platform underpinned by blockchain technology. It’s supported by major industry players with 94 firms having signed up to the ecosystem so far. More than 154 million shipping events have been captured on the platform so far and the project has now moved from pilot to live running with early adopters.
10 of the world’s biggest companies, including Walmart Inc. and Nestlé SA, are building Food Trust, a blockchain ecosystem holding data about harvests, processing, packaging and shipping to remake how the industry tracks food worldwide. The purpose is to avoid crises like the recent US case of an E Coli contamination of romaine lettuce across 35 states that left 5 dead and 197 sick. Instead of days and weeks the new system allows trace-backs in seconds.
The technology will simplify and improve real-time visibility and transparency in trading ecosystems. It is relevant to all sectors from health to real estate, from manufacturing to finance, professional services and government systems too. Think reinvention. Think mutable business.
Quotes
“TradeLens uses blockchain technology to create an industry standard for the secure digitization and transmission of supply chain documents around the world. This initiative will generate tremendous savings for our industry over time while enhancing global supply chain security.”
Peter Levesque, CEO of Modern Terminals
“Just as electricity changed the nineteenth century, AI, crypto, and Blockchain are changing the twenty-first. Disrupting the organizational principles that historically have powered the world economy’s business models infrastructure. These ideas and foundational technologies promise to change the very structure of human interaction. Faster than ever!”
Dinis Guarda – CEO Lifesci and Ztudium, top 10 blockchain influencer
Around 90% of North American and European banks are already exploring blockchain, but all sectors are gearing up, so the skills and development resources already command a premium. Cloud and blockchain technology work naturally together, with a choice of Blockchain as a Service providers allowing global access to distributed resources, low-cost entry for test environments, pay as you use pricing, and then the ability to scale for high performance. If you haven’t already, you should make sure your internal resources are blockchain literate. Choose a blockchain platform provider for your first proof of concept and incorporate the revised blockchain business model thinking in to your transformation strategy as soon as you can.
The Bottom Line
Ignore the hype, but in spite of the noise, we believe blockchain will change or disrupt all sectors of business over the next 20 years. You need to skill up and start planning it into your technology strategy now.
Solutions
Coming soon.


